855-394-2121
855-394-2121

When you're in the market for a new HVAC system, you may come across terms like SEER (SEER2) and EER (EER2). But what exactly do these acronyms mean, and why should you care about them? Below you can find the answer:
SEER stands for Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio. It's a rating that measures the cooling efficiency of an air conditioner or heat pump. SEER is calculated by dividing the total cooling output of the system over a typical cooling season by the total electric energy input during the same period. In simpler terms, SEER tells you how efficiently your HVAC system can cool your home during the summer.
SEER = (1 × EER100% + 42 × EER75% + 45 × EER50% + 12 × EER25%)/100
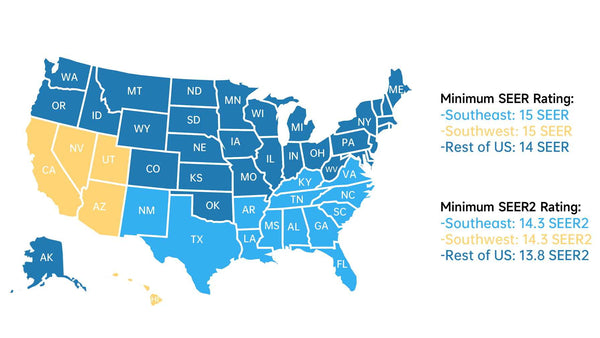
Federal minimum the rating standards vary based on temperature and locality by state. According to SEER standards, the colder, northern states have required a system to be 13 SEER minimum. While southern, southeastern and southwestern states have been held to a slightly higher minimum SEER of 14. From January 2023, these minimum standards are increased nationally and replaced by SEER2 rating, which is about 4.5% lower than the SEER.
Here is the minimum standards comparison of the SEER vs SEER2 rating:
Now, let's compare SEER with another term you might encounter, EER. EER stands for Energy Efficiency Ratio and provides a snapshot of the system's efficiency at a specific operating condition, such as 95°F outdoor temperature, indoor temperature of 80℉, or 50% relative humidity. This means that EER doesn't consider the system's performance over an entire season, making it less comprehensive than SEER. SEER is a more accurate representation of how well your HVAC system will perform throughout the year, including during milder weather, while EER is helpful for understanding how well your system will handle extreme heat.
EER is calculated by dividing the cooling capacity (in BTUs) by the electrical power input (in watts) at a fixed outdoor and indoor temperature.
EER = BTUcooling/W
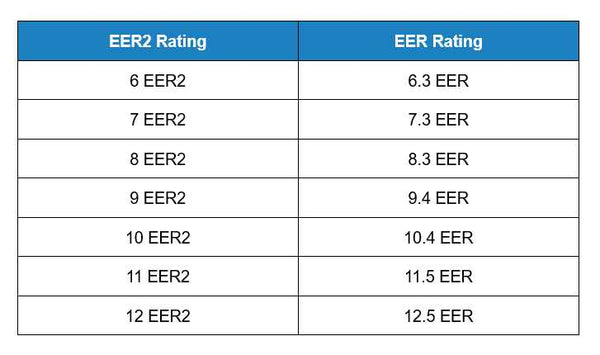
From Jan. 1, 2023, EER2 becomes the latest version that replace with EER. The main difference between them is they use different test conditions:
EER2 ratings are 4.1% lower than EER ratings. Here are some examples of their conversion:
Understanding SEER2 and EER2 is crucial for you if you plan to upgrade your HVAC systems for several reasons:
💡Energy Efficiency: Higher SEER2 and EER2 ratings indicate greater energy efficiency, which can result in lower energy bills. Like InverterCool heat pumps, they can achieve up to 17 SEER2 and help you save up to 40% on your energy bills each year.
💡Environmental Impact: More energy-efficient HVAC systems are better for the environment, as they reduce greenhouse gas emissions. By selecting a system with a high SEER2 or EER2 rating, you can contribute to a greener planet.
💡Long-Term Savings: Investing in a system with a higher SEER2 and EER2 can lead to long-term savings. Although efficient systems may have a higher upfront cost, their reduced energy consumption can pay off over time.
💡Comfort: Systems with higher SEER2 and EER2 ratings tend to provide better and more consistent cooling and heating, ensuring greater comfort for home.
In conclusion, SEER2 and EER2 are important metrics for homeowners to consider when purchasing an HVAC system. These ratings can help you make informed decisions that lead to energy savings, environmental benefits, and overall comfort in your home.
If you're in the market for a new HVAC heat pump system or have any questions about an HVAC company near me in Florida and California, don't hesitate to contact InverterCool at 855-394-2121, our experts are here to assist you in finding an efficient and higher SEER2 heating and cooling system.
Leave a comment